Cron Job & Cron Expressions Guide
What is Cron Job?
The cron command line utility, also known as cron job, is a job scheduler on Unix-like operating systems. Users set up and maintain software environments that use cron to schedule jobs to run periodically at fixed times, dates, or intervals.
Advantages of using Cron Job
One of the hardships of sysadmins is probably having to do tasks day and night. Some tasks need to be done overnight, or must be done on weekends. So we have to spend our free time every night to run commands and scripts after hours? Or do you always have to stay up at night to run backups or updates?
Thanks to Cron Job, you will save a large amount of time when scheduling repeated tasks, without having to try to remember and create recurring jobs over and over again.
Limitations when using Cron Job
Cron Jobs can only execute commands in cycles of 1 minute or more. In case you want to perform repetitive tasks in cycles less than 1 minute, it will not be possible.
Cron Job Components
A cron job consists of two main components:
- Cron Expression: Indicates the job repetition cycle
- Command: The command that will be executed
Understanding Cron Expressions
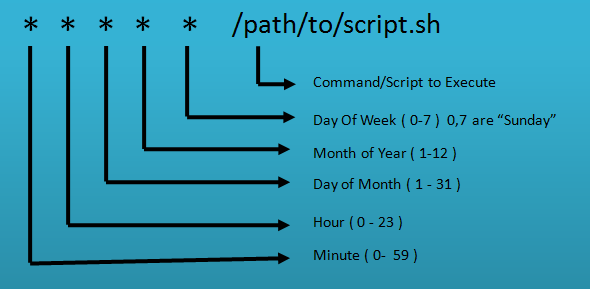
As you can see in the image above, * * * * * is the Cron expression.
Basic Structure
A cron expression consists of 5 fields separated by spaces:
┌───────────── minute (0 - 59)
│ ┌───────────── hour (0 - 23)
│ │ ┌───────────── day of the month (1 - 31)
│ │ │ ┌───────────── month (1 - 12)
│ │ │ │ ┌───────────── day of the week (0 - 6) (Sunday to Saturday)
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
* * * * *Field Values and Ranges
| Field | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Minute | 0-59 | Which minute of the hour |
| Hour | 0-23 | Which hour of the day (24-hour format) |
| Day of Month | 1-31 | Which day of the month |
| Month | 1-12 | Which month of the year (or JAN-DEC) |
| Day of Week | 0-6 | Which day of the week (0=Sunday, or SUN-SAT) |
Special Characters
Asterisk (*)
- Meaning: All values within the allowed range
- Examples:
*in minute field = every minute*in hour field = every hour*in day field = every day
Comma (,)
- Meaning: List separator for multiple values
- Examples:
7,19in hour field = 7 AM and 7 PM1,15in day field = 1st and 15th of the monthMON,WED,FRIin day of week field = Monday, Wednesday, Friday
Hyphen (-)
- Meaning: Range of values
- Examples:
7-19in hour field = from 7 AM to 7 PM1-5in day of week field = Monday to FridayJAN-MARin month field = January to March
Slash (/)
- Meaning: Step values (intervals)
- Examples:
*/5in minute field = every 5 minutes0-20/2in hour field = every 2 hours from midnight to 8 PM*/3in month field = every 3 months
Question Mark (?)
- Meaning: No specific value (used in day of month or day of week)
- Usage: When you want to trigger on one but not the other
Month and Day Names
You can use names instead of numbers:
Months: JAN, FEB, MAR, APR, MAY, JUN, JUL, AUG, SEP, OCT, NOV, DEC
Days: SUN, MON, TUE, WED, THU, FRI, SAT
Special Strings
Instead of the five fields, you can use these special strings:
| String | Meaning | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| @yearly or @annually | Run once a year | 0 0 1 1 * |
| @monthly | Run once a month | 0 0 1 * * |
| @weekly | Run once a week | 0 0 * * 0 |
| @daily or @midnight | Run once a day | 0 0 * * * |
| @hourly | Run once an hour | 0 * * * * |
| @reboot | Run at startup | N/A |
Common Cron Expression Examples
Basic Timing
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
* * * * * | Every minute |
0 * * * * | Every hour (at minute 0) |
0 0 * * * | Every day at midnight |
0 0 * * 0 | Every Sunday at midnight |
0 0 1 * * | First day of every month at midnight |
0 0 1 1 * | Every January 1st at midnight |
Specific Times
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
30 2 * * * | Every day at 2:30 AM |
0 9 * * 1-5 | Every weekday at 9:00 AM |
0 22 * * 1-5 | Every weekday at 10:00 PM |
0 0,12 * * * | Every day at midnight and noon |
15 2,6,10,14,18,22 * * * | Every day at 2:15, 6:15, 10:15, 14:15, 18:15, 22:15 |
Intervals
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
*/5 * * * * | Every 5 minutes |
0 */2 * * * | Every 2 hours |
0 0 */3 * * | Every 3 days |
0 0 1 */2 * | Every 2 months on the 1st |
0 9-17 * * 1-5 | Every hour from 9 AM to 5 PM, Monday to Friday |
Advanced Examples
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
23 0-20/2 * * * | At 23 minutes past every 2nd hour from midnight to 8 PM |
0 4 8-14 * * | At 4:00 AM on every day-of-month from 8 through 14 |
0 0 1,15 * 3 | At midnight on the 1st and 15th of every month, and every Wednesday |
5 0 * 8 * | At 12:05 AM every day in August |
15 14 1 * * | At 2:15 PM on the first day of every month |
Real-World Use Cases
| Expression | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
0 2 * * * | Daily at 2:00 AM | Database backups |
0 0 * * 0 | Weekly on Sunday midnight | Weekly reports |
*/15 * * * * | Every 15 minutes | System health checks |
0 0 1 * * | Monthly on 1st at midnight | Monthly billing |
0 9 * * 1 | Every Monday at 9:00 AM | Weekly team meetings |
0 */6 * * * | Every 6 hours | Log rotation |
30 2 * * 1-5 | Weekdays at 2:30 AM | Business day maintenance |
Testing Your Cron Expressions
Online Tools
- Crontab Guru - Simple cron expression validator
- Cron Expression Generator
Command Line Testing
# Test if your cron syntax is valid
echo "0 2 * * * /path/to/script.sh" | crontab -
# List current crontab
crontab -l
# Edit crontab
crontab -eBest Practices
1. Be Specific About Timing
# Good: Specific time
0 3 * * * /backup.sh
# Avoid: Too frequent without purpose
* * * * * /script.sh2. Use Absolute Paths
# Good
0 2 * * * /usr/bin/php /var/www/app/backup.php
# Bad
0 2 * * * php backup.php3. Handle Output Properly
# Redirect output to avoid email spam
0 2 * * * /backup.sh > /var/log/backup.log 2>&1
# Send only errors to email
0 2 * * * /backup.sh > /dev/null4. Consider Server Load
- Avoid scheduling all jobs at the same time (e.g., all at midnight)
- Stagger similar jobs across different times
- Use random delays for distributed systems
Common Pitfalls
1. Day of Month vs Day of Week
When both day of month and day of week are specified (not *), the job runs when EITHER condition is met:
# This runs on the 15th of every month AND every Friday
0 0 15 * 5
# To run only on Friday the 15th, use:
0 0 15 * * [ $(date +\%u) -eq 5 ] && /script.sh2. Month Boundaries
# Be careful with day 31 - doesn't exist in all months
0 0 31 * * /script.sh # Won't run in February, April, June, etc.3. Timezone Considerations
- Cron runs in the system timezone
- Consider daylight saving time changes
- Document timezone assumptions
Practice Exercises
Try to figure out what these expressions mean:
0 0,12 1 */2 *- ?0 4 8-14 * *- ?0 0 1,15 * 3- ?5 0 * 8 *- ?15 14 1 * *- ?*/10 9-17 * * 1-5- ?0 2 * * 1,3,5- ?30 */3 * * *- ?
Answers:
- At midnight and noon on the 1st day of every 2nd month
- At 4:00 AM on every day from 8th to 14th of every month
- At midnight on the 1st and 15th of every month, and every Wednesday
- At 12:05 AM every day in August
- At 2:15 PM on the 1st day of every month
- Every 10 minutes from 9 AM to 5 PM, Monday to Friday
- At 2:00 AM on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday
- At 30 minutes past every 3rd hour
Troubleshooting Cron Jobs
Check if Cron is Running
sudo systemctl status cron
# or
sudo service cron statusView Cron Logs
# On most systems
sudo tail -f /var/log/cron
# On Ubuntu/Debian
sudo tail -f /var/log/syslog | grep cronCommon Issues
- Path Problems: Always use absolute paths
- Environment Variables: Cron has minimal environment
- Permissions: Ensure the user can execute the command
- Output Handling: Redirect output to prevent issues
This comprehensive guide should help you master cron expressions and create effective scheduled tasks!