Systemd Service
What is Systemd Service?
Systemd is a service management and boot system for Linux operating systems. It is designed to start, manage, and monitor services and other system resources.
Here are some basic concepts about Systemd:
Unit: This is a basic component in Systemd. Each unit is a configuration for a certain type of object in the system (service, hard drive, mount point, ...). Common unit types include:
- Service unit (
.service): Manage services (daemons) in the system. - Socket unit (
.socket): Manages sockets, often combined with a service unit to start services based on network activity. - Target unit (
.target): Groups units together, representing a specific state of the system (eg multi-user.target, graphical.target). - Mount unit (
.mount): Manages mounting the file system.
- Service unit (
Service File: This is the configuration file for service units, located in the
/etc/systemd/system/or/lib/systemd/system/directory. A service file includes the following main parts:[Unit]: Describes the service and defines dependencies.[Service]: Set parameters related to service execution.[Install]: Defines how the service will be enabled or disabled.
Example of a simple service file:
[Unit] Description=Simple service test [Service] ExecStart=/bin/bash -c "echo Simple service - start && sleep 60 && echo Simple service - end" [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetSystemd management commands:
systemctl start <service>: Start the service.systemctl stop <service>: Stop the service.systemctl restart <service>: Restart the service.systemctl enable <service>: Enable the service to automatically start when the system boots.systemctl disable <service>: Disable the service.systemctl status <service>: Check the status of the service.journalctl -xe: View systemd logs.
Journal: Systemd uses
journaldto record system logs. You can usejournalctlto view these logs.
Systemd has become an important part of many Linux operating systems, providing powerful and flexible service management capabilities.
Service Unit Management
In systemd, a "Service Unit" is a special unit used to define and manage system services. Managing service units is an important part of a system administrator's job to ensure that services operate stably and efficiently.
Service management main screen
At the main screen of the server management page: Select Services 
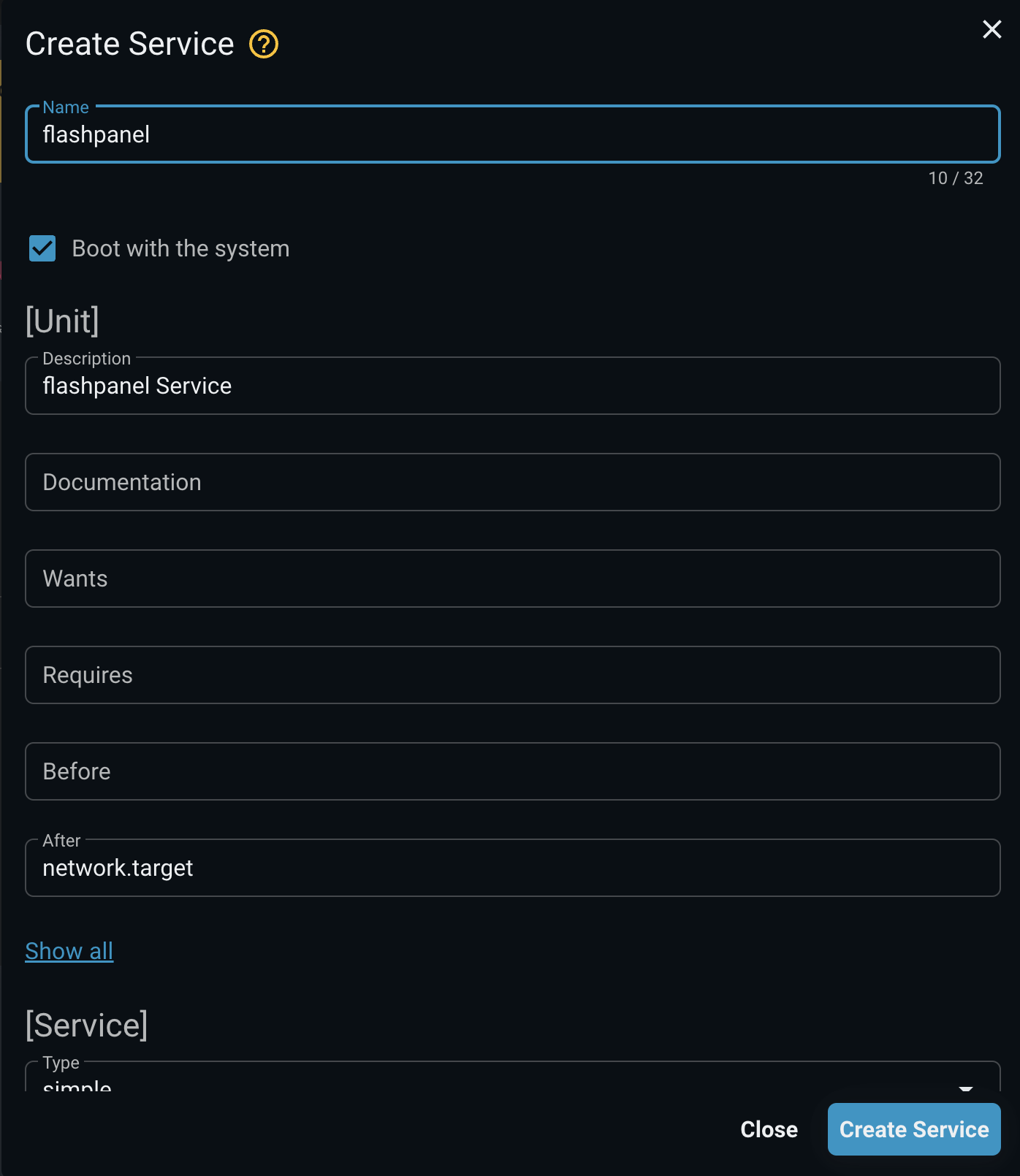
Create and Configure Service Unit:
Steps to create and configure a service:
At the service management screen:
- Select Add new service
- Fill in service information
- Click the Add service button
Edit Service Unit configuration:
Steps to edit the configuration of a service follow the instructions in the following image:
At the main server management screen:
- Click on the pencil icon next to the service you want to edit
- Fill in the service information that needs to be corrected or supplemented
- Click the Edit service button
Other actions on the service management home screen:
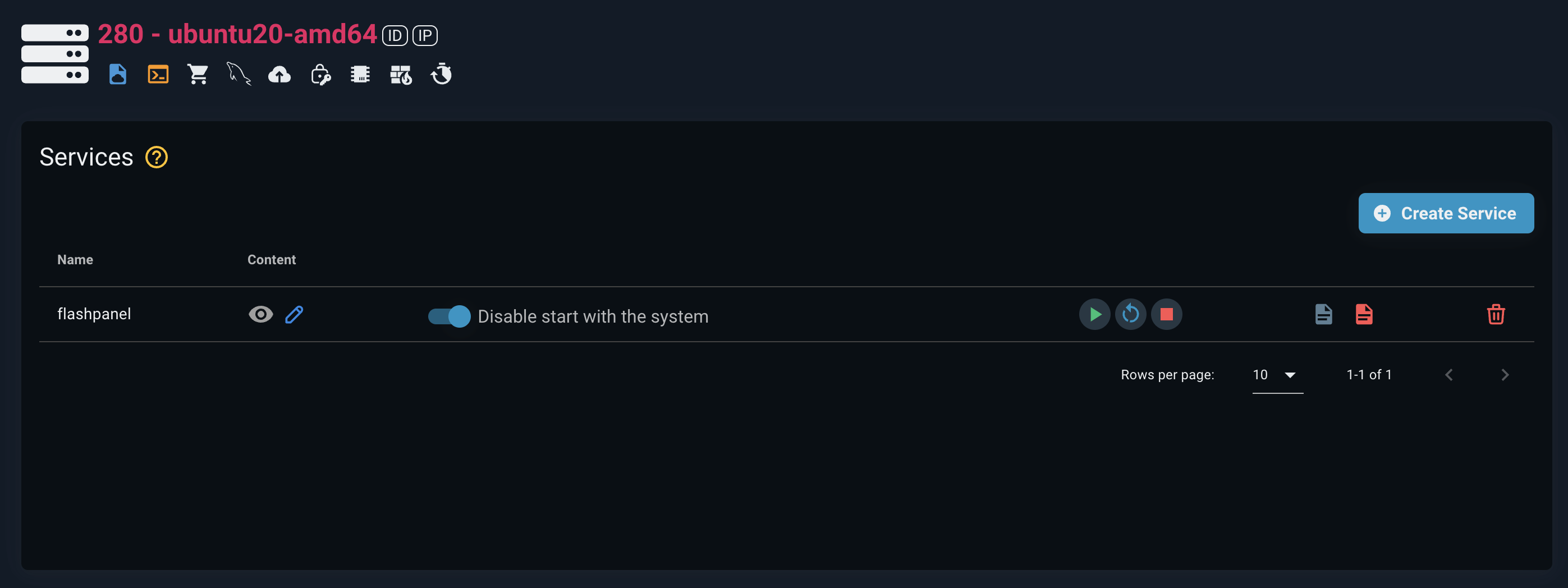
- Start service
- Restart service
- Stop service
- View normal log
- View service error log
- Enable the service to automatically start when the system boots
- Deactivate the service that automatically starts when the system boots (I have to start it manually when the system boots)
- Delete service
Summary:
Above are the basic and quite easy steps to add, edit, and manage a service you create yourself.