CronJob Scheduling (Schedule)
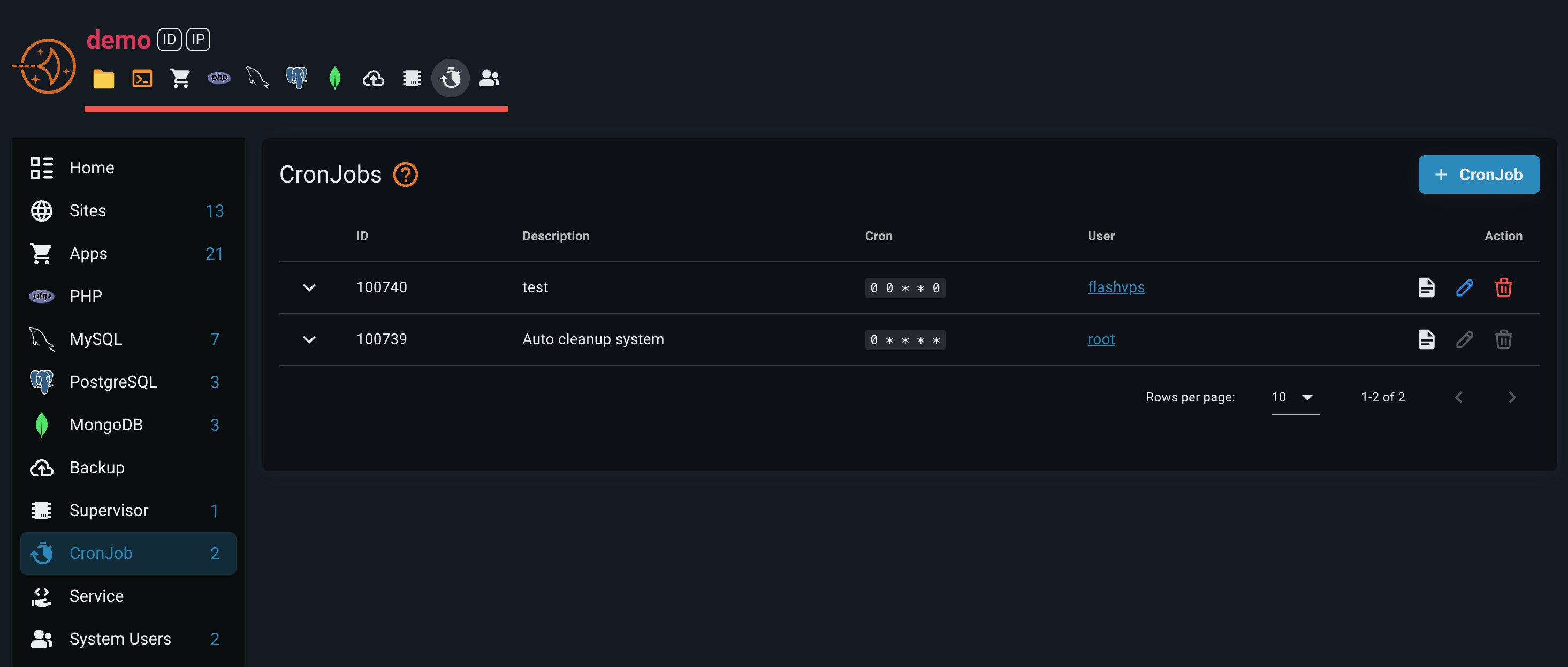
Overview
The CronJob scheduling feature in FlashPanel allows you to automate server operations by executing shell commands at specified intervals. This powerful automation system supports routine maintenance, backups, updates, and custom scripts, making server management more efficient and reliable.
Key Features
- Flexible Scheduling: Support for standard cron expressions with visual editor
- User Context: Execute commands under specific Linux users
- Real-time Monitoring: Live execution logs and status tracking
- Template Library: Pre-defined templates for common scheduling patterns
- Custom Scripts: Integration with custom script library
- AI-Powered Descriptions: Automatic description generation for commands
Creating a Scheduled Job
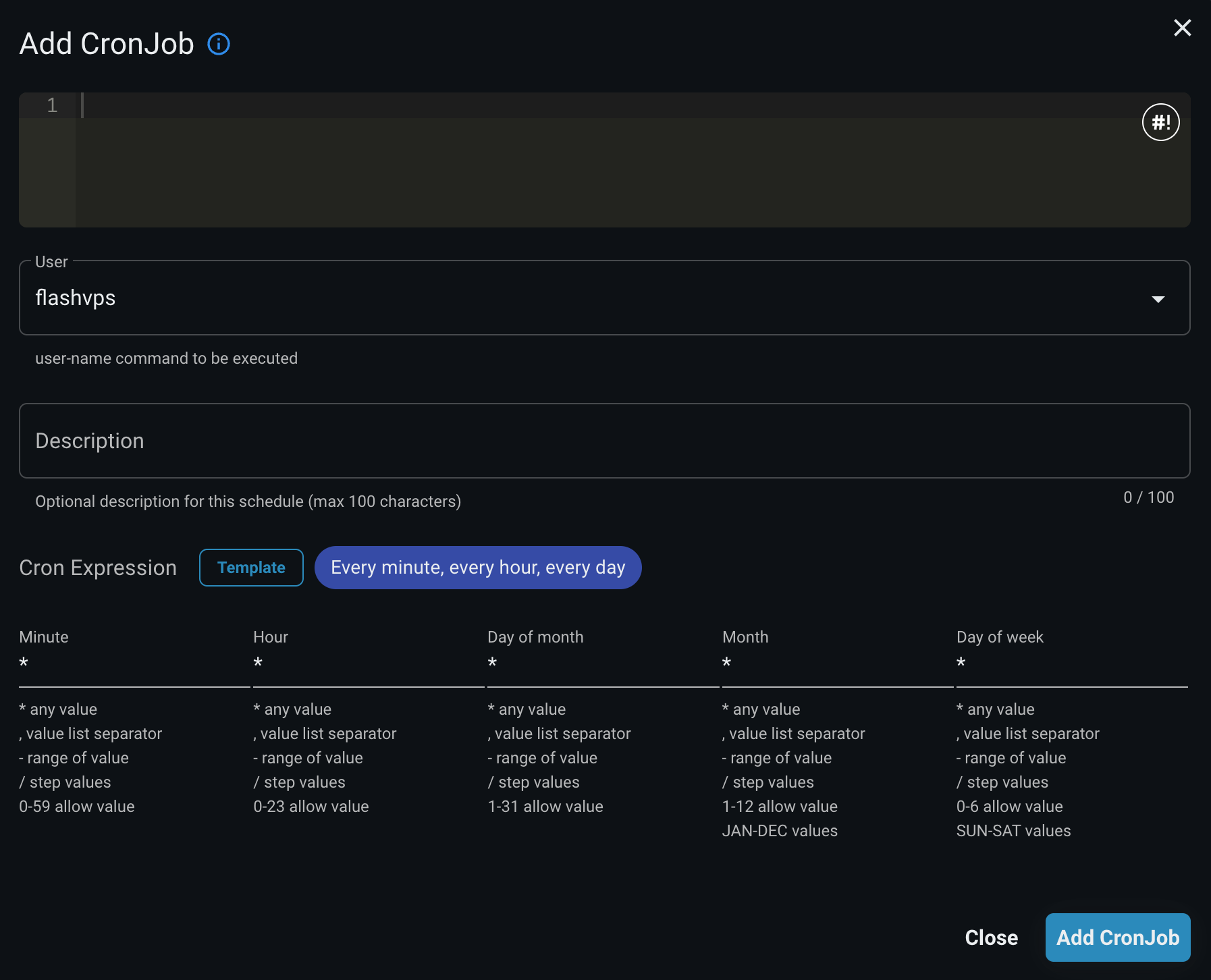
You can create scheduled jobs through the FlashPanel console via the CronJobs tab in your server's management console.
Required Information
When creating a new scheduled job, you need to provide:
Command: The shell command to execute
bash# Example: Laravel artisan command php /home/flashpanel/default/artisan schedule:run # Example: Database backup mysqldump -u root -p$DB_PASSWORD mydatabase > /backups/db_$(date +\%Y\%m\%d).sql # Example: Log cleanup find /var/log -name "*.log" -mtime +7 -deleteUser: System user that will execute the command (e.g.,
flashpanel,root)Cron Expression: Defines when and how often the command runs
Description: Optional description for easy identification (max 100 characters)
Cron Expression Builder
The system provides an intuitive cron expression builder with:
📚 Want to learn more about Cron Expressions?
For a comprehensive guide to cron expressions, syntax, examples, and best practices, visit our detailed Cron Job & Expressions Guide.
Visual Editor
Five input fields representing:
- Minute (0-59)
- Hour (0-23)
- Day of Month (1-31)
- Month (1-12 or JAN-DEC)
- Day of Week (0-6 or SUN-SAT)
Predefined Templates
| Template | Cron Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Every Minute | * * * * * | Runs every minute |
| Hourly | 0 * * * * | Runs at the start of each hour |
| Nightly | 0 0 * * * | Runs daily at midnight |
| Weekly | 0 0 * * 0 | Runs every Sunday at midnight |
| Monthly | 0 0 1 * * | Runs on the 1st of each month |
| Yearly | 0 0 1 1 * | Runs on January 1st |
| On Reboot | @reboot | Runs once at system startup |
Real-time Explanation
The system provides instant feedback showing when your cron job will execute in human-readable format.
Managing Scheduled Jobs
Viewing Jobs
All scheduled jobs are displayed in a comprehensive table showing:
- ID: Unique identifier
- Description: Job description or auto-generated summary
- Cron: Expression with tooltip explanation
- User: Linux user executing the command
- Actions: Available operations
Available Actions
View Command Details
Click on any row to expand and view the full command in a syntax-highlighted editor.
Edit Job
Modify existing jobs using the same interface as creation, with all current values pre-populated.
View Logs
Access execution logs to monitor job performance and troubleshoot issues. Logs include:
- Command output
- Error messages
- Execution timestamps
- Exit codes
Delete Job
Remove scheduled jobs with confirmation dialog to prevent accidental deletion.
Common Use Cases
Laravel Applications
For Laravel applications using Laravel's task scheduling, create a job that runs every minute:
# Command
php /path/to/your/laravel/app/artisan schedule:run
# Cron Expression
* * * * *
# User
flashpanelDatabase Backups
# Daily MySQL backup at 2 AM
mysqldump -u root -p$DB_PASSWORD database_name > /backups/db_$(date +\%Y\%m\%d).sql
# Cron Expression
0 2 * * *System Maintenance
# Weekly system updates on Sunday at 3 AM
apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y
# Cron Expression
0 3 * * 0Log Management
# Daily cleanup of old log files
find /var/log -name "*.log" -mtime +30 -delete
# Cron Expression
0 1 * * *Application Cache
# Hourly cache clearing
php /var/www/html/artisan cache:clear
# Cron Expression
0 * * * *Advanced Features
Custom Script Integration
Select from your custom script library when creating scheduled jobs, allowing you to reuse tested commands across multiple schedules.
AI-Powered Descriptions
The system can automatically generate descriptive names for your commands using AI analysis, making it easier to identify jobs at a glance.
Real-time Updates
All changes are reflected in real-time through WebSocket connections, ensuring your team sees updates immediately.
User Permissions
Jobs can be executed under different Linux users, providing proper permission isolation and security.
Troubleshooting
Job Not Running?
If your scheduled job isn't executing:
- Check Command Path: Ensure all paths are absolute and correct
- Verify Permissions: Make sure the specified user has necessary permissions
- Review Logs: Check the job logs for error messages
- Test Command: Run the command manually as the specified user
- Validate Cron Expression: Use the built-in explanation to verify timing
Common Issues
Path Problems
# Wrong (relative path)
php artisan schedule:run
# Correct (absolute path)
php /home/flashpanel/myapp/artisan schedule:runPermission Errors
# Ensure the user has access to required directories
# Check file ownership and permissions
ls -la /path/to/your/scriptEnvironment Variables
# Commands may need full environment setup
/bin/bash -l -c "source ~/.bashrc && your_command"Security Considerations
- Always use absolute paths in commands
- Run jobs with minimal required privileges
- Avoid storing sensitive data in command strings
- Use environment variables for credentials
- Regularly review and audit scheduled jobs
- Monitor job execution logs for suspicious activity
Best Practices
- Use Descriptive Names: Add clear descriptions to identify jobs easily
- Test Commands: Always test commands manually before scheduling
- Monitor Logs: Regularly check execution logs for errors
- Use Appropriate Users: Choose the right Linux user for each task
- Backup Critical Jobs: Document important scheduled tasks
- Avoid Overlapping: Ensure long-running jobs don't overlap
- Handle Failures: Include error handling in your scripts
- Regular Cleanup: Remove unused or obsolete jobs
The CronJob scheduling feature provides a robust foundation for server automation, helping you maintain efficient and reliable server operations with minimal manual intervention.